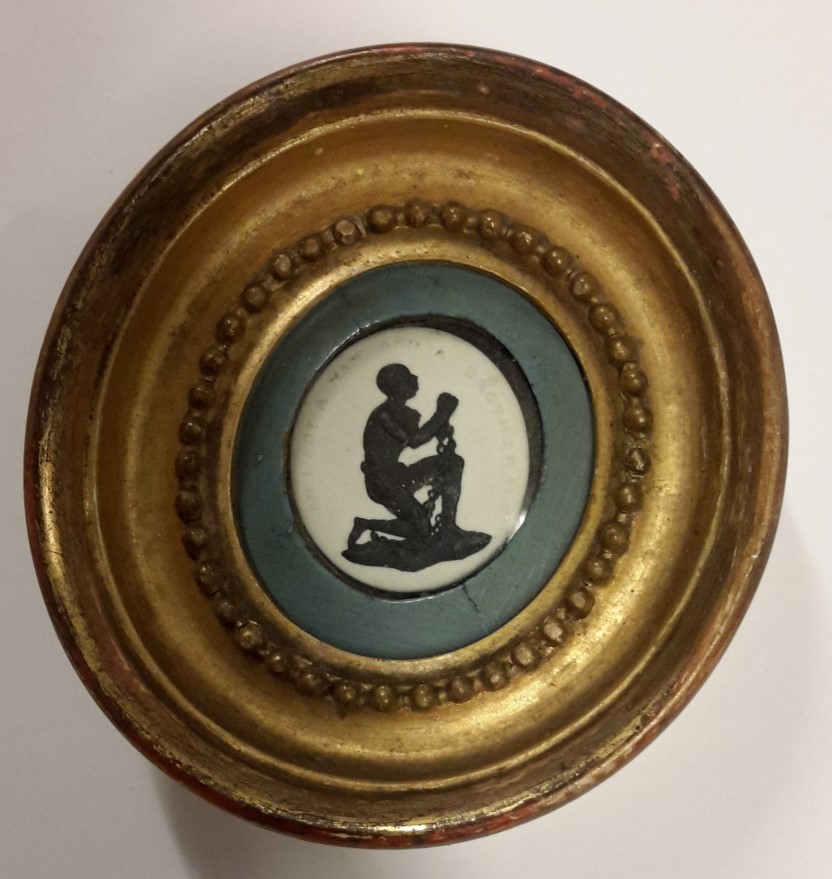
On 31st January 1823 a group calling itself the Committee on Slavery assembled at the Kings Head Tavern, Poultry, in the City of London. William Smith M.P. was in the Chair and those present included Zachary Macaulay, Samuel Hoare, Thomas Clarkson, Samuel Gurney, Thomas Babington, Thomas Hodgkin and William Wilberforce junior. The committee agreed that it was ‘deeply impressed with the magnitude and number of the evils attached to the system of slavery which prevails in many of the colonies of Great Britain, a system which appears … to be opposed to the spirit and precepts of Christianity as well as repugnant to every dictate of natural humanity and justice’ and resolved to found an association ‘for mitigating and gradually abolishing the state of slavery throughout the British dominions’ (MSS. Brit. Emp. s. 20, E2/1, pages 1-2).

Opening page of the first minute book of the Anti-Slavery Society, MSS. Brit. Emp. s. 20, E2/1, page 1 [click to enlarge]. © Anti-Slavery International To mark the organisation’s bicentenary the minute book has been digitised and is now available from Bodleian Archives & Manuscripts and Digital Bodleian.
This was the beginning of a campaigning organisation, the successor of which is still in existence today, two hundred years later. The Committee on Slavery changed its name a number of times during the 19th century but came to be known as the Anti-Slavery Society and extended its focus from British territories to a commitment to end slavery worldwide. It merged in 1909 with the Aborigines Protection Society (founded in 1837) which campaigned against the ill-treatment of indigenous peoples. In 1990 the Society changed its name to Anti-Slavery International and continues to campaign against modern slavery, forced labour and human trafficking.
The Society’s archive was purchased for the Bodleian Library in 1951, with further tranches of papers added in later decades, and is available for consultation in the Weston Library. The archive includes:
- minute books from 1823 to 1935
- long runs of correspondence from many parts of the world, bringing examples of slavery to the Society’s attention
- correspondence with government departments
- territorial files
- lantern slides and photographs
- financial papers
- newspaper cuttings and printed ephemera
- the records of associated groups such as the Mico Charity, the Committee for the Welfare of Africans in Europe and the British Armenia Committee
The Bodleian also holds The Anti-Slavery Reporter, published by the Society since 1825 with various changes of title.
The archive records key events during the Society’s history including the organisation of the first World Anti-Slavery Convention in London in 1840, the campaign against the atrocities perpetrated against enslaved labourers in the Congo and in Peru, the lobbying of the League of Nations and later the United Nations leading to international agreements to end slavery and the promotion of human rights for indigenous peoples. The Society’s work had a global reach from the apprenticeship system in the Caribbean, forced labour in Russian timber camps and pass laws in Africa to lynching in America and Mui Tsai in China and southeast Asia.
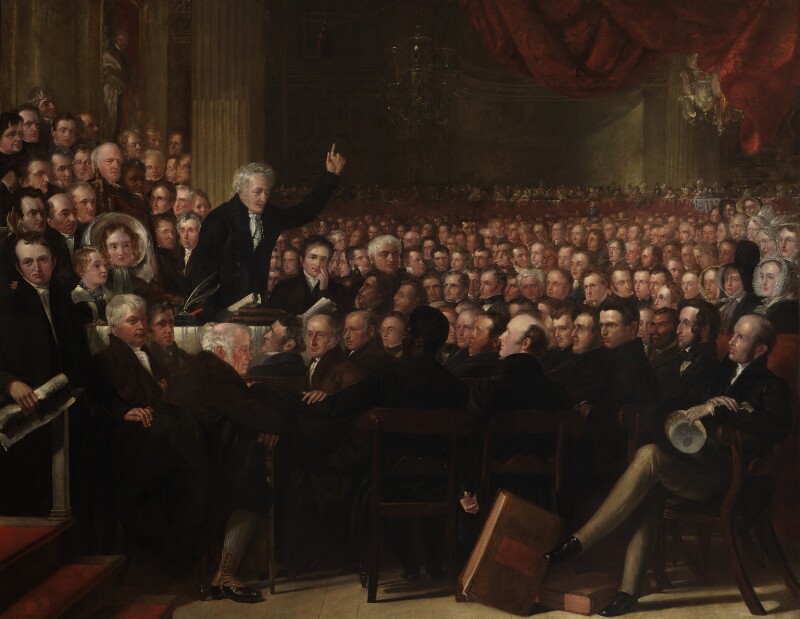
The Anti-Slavery Society Convention in 1840 by Benjamin Robert Haydon. Oil on canvas, 1841. NPG 599. © National Portrait Gallery, London. CC BY-NC-ND 3.0
To mark the organisation’s bicentenary the minute book recording the first meeting has been digitised and is now available from Bodleian Archives & Manuscripts and Digital Bodleian.
